There has been a lot of buzz surrounding cryptocurrency and blockchain, mostly due to the potential high sums of money that can be made in the industry. Recently, though, a lot of that attention has shifted to the applications of this technology across other industries.
Niches have emerged around this shift, including blockchain solutions providers, Initial Coin Offering (ICO) third parties, blockchain educators, software client developers and more. While the technology has made its way into industries such as logistics, agriculture, education, real estate, gaming technology and even commerce, the one link between them all is the finance industry.
The finance industry is mostly traditional in its approach towards global money operations and due to how sensitive the issue of money is, adoption of new technology is often slow. In fact, since American banks began issuing credit cards in 1950 and accepting electronic deposits in 1975, all new technology has been built around these events. Blockchain technology in the form of Bitcoin is perhaps the first drastic form of innovation in money handling since then.
Unfortunately, not everyone sees Bitcoin as a good thing, with several people calling it a bubble and likening it’s potential doom to the dotcom era. Either way, the buzz generated by cryptocurrency and its underlying technology is one that hasn’t been heard of in the world of finance in a long time.
The finance world is built on the concept of access to money that central authorities control. Blockchain technology, on the other hand, takes consensus away from central authorities and places it in the hands of the network users.
This ensures that people no longer have to depend on the fees associated with third-party bank clients as well as intermediaries in various industries. The concept itself goes against the way traditional banking is done in different parts of the world.
For this reason, several banks and large corporations are opposed to the mainstream adoption of blockchain technology as the future of money. It may potentially disrupt the industry, change the face of investment and banking as well as render several banking methods obsolete. This type of change would force these corporations to either embrace a blockchain-driven approach to their operations or face being left behind by the rest of the world.
As a result, some corporations like Amazon, J.P.Morgan, and IBM have already developed solutions that incorporate blockchain services into their list of operations. The third party finance solutions providers are not left behind either. Visa card and Mastercard have already been making their foray into the blockchain industry since 2016, announcing several patents and services along the way.
This move to blockchain by companies like Mastercard and Visa are even more significant because they are among the corporations that have held skeptical views regarding Bitcoin and other altcoins. This view is partly due to the lack of regulation for these coins and such companies will not back altcoins unless the government backs them. Despite their technological advancements in that direction, their views towards Bitcoin have not changed. Blockchain, on the other hand, is the underlying technology behind these cryptocurrencies and can be applied in many different ways.
Mastercard Blockchain Projects
Since its inception, Mastercard has played a pivotal role in the global finance industry. The financial solutions giant has been instrumental in the issuance, maintenance, and functionality of Mastercard credit cards and debit cards. It has also created innovative payment solutions like Maestro and campaigns like ‘Priceless.’
Globally, Mastercard debit and credit cards have become commonplace in the hands of citizens, irrespective of what they do. In a time when only 8% of the total money on earth exists as paper, Mastercard has carved a significant niche for itself.
Now, the company has taken huge strides towards blockchain, what several people have termed “the future of money.” Currently, Mastercard holds up to 30 Blockchain related patents including an identity verification patent, a patent for anonymous transactions and a system that links cryptocurrency with a fiat account.
Despite the progress that the company has made, it is apparent that there is still ongoing research into more innovative applications of blockchain technology within its walls. In due time, more of those applications may be brought to light.

About Mastercard
Mastercard first emerged in 1966 as the Interbank Card Association (ICA), a group of banks came together with the aim of leading innovation in the banking sector. Subsequently, ICA acquired the Master Charge name as well as the ‘interlocking circles’ trademark and changed the Master Charge name to Mastercard.
Since its emergence, the company has reached several significant milestones. Mastercard was the first company to issue a payment card in the People’s Republic of China as well as the first company to use a laser hologram on cards and the first payments company to launch a business card.
In the 1990s, Mastercard partnered with Europay International to launch the first online debit program in the world, known as Maestro. The program was a success and has stood the test of time, just like the company itself.
Following the Maestro launch, the corporation launched its ‘Priceless’ campaign along with “Mastercard advisors”, an organization that focused on providing payment solutions and professional services on a global scale. Owing part of the success of Maestro, Mastercard integrated with Europay in 2002 to become a private share corporation.
In 2006, Mastercard made its full transition into a corporate ownership and governance structure, listing its stock on the New York Stock Exchange. Subsequently, Europay France and Mastercard Europe concluded plans to integrate their operations and Mastercard acquired Orbiscom. In 2009, the company began its plans to also acquire DataCash (the prepaid program management business of Travelex, Truaxis, and Trevica).
By 2010, the company had become one of the most innovation-driven corporations in the financial space. To further their research and technology, Mastercard Labs was established to serve as an incubator for new ideas and concepts in the industry.
Subsequently, between 2013 and 2016, Mastercard introduced its new service known as Masterpass and partnered with eServGlobal and Bics to establish HomeSend. Acquisitions made within that period include C-SAM, ElectraCard Services (ECS), Provus, 5One, Vocalink, Applied Predictive Technologies (APT), the Payment Gateway Services business of Transaction Network Services (TNS) and Pinpoint.
In 2016, Mastercard announced its first blockchain patent, marking its foray into the cryptocurrency industry despite earlier reservations. A year after Mastercard announced its acquisition of NuData Security, as well as Brighterion for the enhancement of artificial intelligence capability. In 2018, Mastercard acquired Oltio to enhance the adoption of digital payments in Africa and the Middle East. The company also partnered with IBM to create Truata, an independent trust that provides a secure approach to data analytics and anonymization.
Mastercard Blockchain
Mastercard has filed over 30 patents for blockchain and cryptocurrency-related projects. One of the most prominent patents is for a blockchain-based payment system which promises to deliver instant payments to merchants, fast-tracking for customers and secure verification of payments.
The patent application which was termed “Method And System For Payment Card Verification Via Blockchain” recounts a method of payment processing, which uses a public blockchain to carry out the secure retrieval and verification of the users’ information.
In the patent description, Mastercard described how vulnerable the currently existing method of “wireless transmission of payment credentials” is. According to the company, bad actors can intercept this transmission, stealing users information and using it for fraudulent activities. Due to the security of the blockchain, the company will use it to convey user’s payment credentials securely, essentially protecting them from theft. Through this means, there will be “minimal participation by the consumer.”
As a result, the entire payment process will be more straightforward for the customer, killing two birds with one stone. Mastercard believes that the provision of an application that can quickly and securely convey information to the point of sale (POS) device without subjecting the customer to any form of stress, is a pressing need in the industry.
This need also extends to the fight against credit card “skimming,” a process by which bad actors pull a customer’s credentials off their cards even when they are securely hidden in a bag. The practice is so common that it can happen to anyone, irrespective of class. It also involves intercepting users’ credentials while they are in the process of being wirelessly transmitted to a POS. This means that while paying for goods using a POS device, hackers can intercept a user’s credit card details while in transit.

The Problem of Skimming
Credit card skimming is a massive problem that companies like Visa and Mastercard have struggled with for a long time. While there are security measures in place to prevent it, people have found new ways to bypass these security measures each time.
A report by the ATM Industry Association has shown that credit card skimming accounts for an annual loss of $2 billion globally. Skimming devices are used at gas stations, ATMs and even POS machines to steal customers’ credentials which allow them to further steal from those customers accounts.
One solution that directly tackles the problem is the use of chip cards, and even with this, the research must continue if the finance industry wants to stay ahead of such bad players. The company has adopted blockchain technology as what may hold the key to the complete eradication of skimming. This is why Mastercard has come up with so many blockchain patents, working round the clock to create these solutions.
How Will the Application Work?
In the patent document, Mastercard described a process to encrypt the information on users’ cards and store it on its public blockchain. Subsequently, two keys– a public and a private key– will be issued. When a user makes a purchase with such a registered card, it will trigger a retrieval request, prompting the system to use the issued keys to decrypt and verify the card information.
Following the announcement of the patent, Ann Cairns, vice chair of Mastercard stated that the company had indeed built a blockchain service that can run the whole network. According to Cairns, the company was careful to identify real use cases of its new technology. It was built with scalability in mind as well as the need to create something that not only solves technical problems but ensures a better user experience.
From Microsoft to Facebook and even IBM, blockchain, has captured the attention of several large corporations. There have been various reasons to capitalize on the technology but the most important one by far is to help improve user experience in many already existing consumer operations.
To date, Mastercard remains one of the most invested companies in blockchain and it continues to research and improve the technology with the single aim of ushering in a new future of money. A future that sees traditional money act like Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies in both structure and function.
Mastercard and Innovation
While the blockchain-related moves by Mastercard may have come unexpected, upon closer inspection into the company’s history, it’s not difficult to see why this direction has been taken.
All through its 50-year existence, the finance solutions giant has shown its staunch dedication to technology-driven innovation. Things like credit cards, which seem simple, took research, time and resources to create and now, most Americans have at least one credit card. Banking has become easier now than it was in the days when most of the money in existence was physical. Along the way, Mastercard has secured partnerships and acquisitions with its innovative goal in mind.
Given the company’s history, it’s safe to say that the blockchain solutions it will create, will indeed make life easier for a significant number of people. The value-driven approach taken by the company would be on a global scale.
Apart from operations, Mastercard has also developed a company culture which encourages innovation in smaller local communities with its STEM programs. Through its network of entrepreneurs and developers, the company continues to do its part to tie the world of banking and commerce together. By focusing on innovation, the company shows that despite its reservations, it will always do what is best for the consumers.
In addition to building new blockchain solutions, Mastercard has also made significant investments into other corporations that share its goal. One example is the Digital Currency Group, a collaborator, and incubator for Bitcoin and blockchain-related tech startups. The company also became a member of the Enterprise Ethereum Alliance (EEA) to broaden its scope using Ethereum’s technology. Mastercard also runs a program called Start Path Global program in which it explores new use cases of blockchain with smaller startups.

How Mastercard is Making Blockchain the Future of Money
Despite blockchain’s many demonstrated use cases, its application in finance has always been critical. It is the underpinning structure that controls the functionality of a cryptocurrency like Bitcoin or Ethereum. The structure consists of a public distributed ledger that allows the currency to exist and change in value without governance or manipulation by a single authority figure. Mastercard has several notable applications, from sending and receiving money to setting budgets via voice assistants and even securely paying employees.
Mastercard Blockchain API
In June 2017, Mastercard created and patented a blockchain program that gives developers the opportunity to build applications on its API. The API is business-to-business (B2B) focused and addresses the problem areas in cross-border payments including speed and transparency.
The API supports both account-based and blockchain-based payments and opens the door to new opportunities in blockchain and a chance to work with corporations such as Apple.
According to Mastercard, there are four major areas which the API addresses:
- Privacy: the company’s blockchain protects the privacy of users by sharing transaction details with only participating members of that transaction. Despite this, the ledger is updated with valid transactions which can be audited at any time.
- Scalability: Mastercard designed its blockchain with the issue of scalability as a major concern. At the moment, only about 1% of the world population is actively involved with cryptocurrency. However, with the massive strides currently being taken within the industry, there will most likely be mainstream adoption in a few years. This is why Mastercard has ensured that there is a good enough processing speed for commercial transactions in place. The system also has extensibility by ensuring that consensus lies between the network users and a trusted network moderator.
- Flexibility: the blockchain API can be used flexibly, including combining it with other Mastercard APIs to create applications. The software development tools provided by the company on its platform can be used in six different languages for ease-of-use.
- Reach: The Mastercard payment network currently includes about 22,000 financial institutions and the company has ensured that its blockchain can seamlessly be integrated with their systems. This will ensure that funds are easily transferred and normal operations are not interfered with.
Mastercard Itinerary Bidding Blockchain Service
Apart from finance, Mastercard has created and patented a blockchain solution for the travel industry. The solution comprises of a bidding platform which allows users to submit their itineraries securely so that travel service providers can bid to satisfy those customers based on the itineraries. As providers including travel companies, airlines and hotels bid, the market becomes more competitive, and users can find the most profitable bids and make plans with those providers.
The patent for the technology was approved by the US Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) in June 2017. This technology provides a way for the global travel industry to become more streamlined and concentrated. The use of bidding ensures that travelers can adjust their itineraries according to the competitive nature of the bids they receive. This saves travelers time as well as money and increases revenue for service providers.

Mastercard Proof of Provenance
Proof of provenance is Mastercard’s way of making the supply chain more transparent for both consumers and wholesalers. The implications of this system will be felt in logistics, food and any industry with a need for the supply of goods. From huge restaurants to ordinary people, consumers can now track the origin of their goods.
Transparency in the supply chain is something that has presented a problem for consumers and wholesalers since the beginning of goods supply. Proof of provenance is a clear way of tracking the exact process of delivery and seeing how and where goods and services reach the consumer. This way, theft, loss, and lack of transparency and accountability in the supply chain can be prevented.
Visa Blockchain Solutions
Just like Mastercard, Visa has been working to improve certain parts of the financial sector. The solutions giant has approached this problem solving by focusing on functionality, user experience, and other relevant areas. The company has prioritized scalability, security, governance, creativity, and interoperability.
With these guiding principles, Visa has designed a platform that will incorporate blockchain technology as its major driving force. The platform will use an API-first strategy to ensure that it is scalable, flexible and user-friendly.
Although Visa does not have nearly as many blockchain patents as Mastercard, its blockchain solution has the potential to make life easier for businesses. Apart from satisfying consumers, Visa’s approach to blockchain technology will hopefully create value for its partners.
About Visa
Visa Inc. is a payments technology solutions company that serves financial consumers, businesses, institutions, and governments globally with fast and secure electronic payments. The VisaNet processing network is one of the fastest in the world with a processing speed of 65,000 transactions per second.
Visa emerged in 1958 as BankAmericard, the first consumer credit card programme for middle-class consumers and small to medium-sized merchants in the U.S., launched by Bank of America. The programme saw subsequent growth and became an international company in 1974.
Following this expansion, its name was changed from BankAmericard to Visa, also issuing the first debit card in 1975. By 2000, Visa had successfully issued 1 billion cards. Other notable milestones include the launch of Visa’s 24-hour ATM, the introduction of electronic signatures and the merger of global businesses that birthed Visa inc. in 2007.
The Initial Public Offering (IPO) that followed was one of the biggest in history. The company also launched the Visa card mobile platform in 2008 with the aim of accelerating the adoption of mobile payments and value-added services. Today, the corporation is one of the biggest players in the financial industry, with operations in over 200 countries and territories. Visa products are tailored to a host of devices, whether for business or personal use.

Visa and Innovation
For a long time, Visa has been a huge driver of innovation in the finance industry. From solutions like the ATM to its modernization of payment technology in African countries, the corporation has managed to stay on top. This is why it is expected that such a company would not miss an opportunity to take advantage of the incredible potential that blockchain technology brings.
In 2016, Visa announced its plans to introduce mVisa in Nigeria as a way to make payments easier for the individuals and businesses that reside there. The solution involves the ability to make payments with the use of QR codes that can be scanned on smartphones. Since the country has over 150 million active smartphone users, it is an excellent alternative to POS device payments.
Visa also digitized payments in Côte d’Ivoire, ensuring that people could carry out seamless payment transactions in a secure and fast way. Now, the tech giant is developing a B2B payment platform which will simplify the entire payment process and eliminate third parties, making it faster and easier for businesses to transfer money. This dedication to innovation has shown time and again that Visa is entirely committed to ensuring the success of global commerce. Its adoption of cryptocurrency is a visible sign of this.
Visa Blockchain
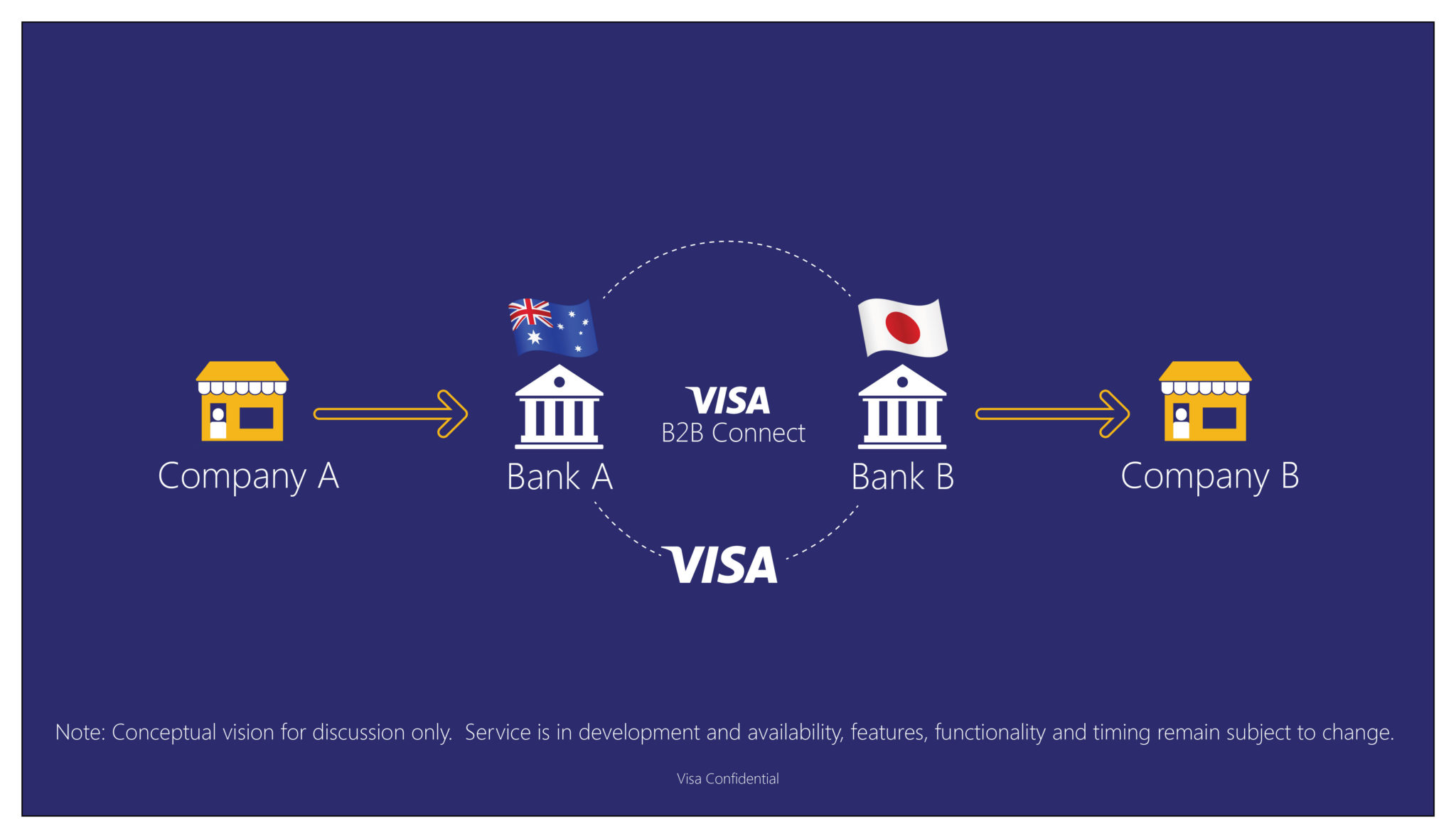
In October 2016, Visa announced its joint venture with Chain, a prominent blockchain enterprise company to develop Visa B2B Connect, a more secure way to process B2B payments on a global scale. The pilot version of the platform launched in 2017 and testing commenced in January 2018.
In August 2017, the United States Patent and Trade Office (USPTO) disclosed the details of Visa’s new blockchain-related patent application. The financial tech giant has shown a broad range of interest in the digital asset industry. However, the patent application signified the importance of Visa’s previously created blockchain platform.
Financial institutions have always faced problems when dealing with third-party clients. The use of these intermediaries during the transfer process can lead to uncertainty and other complications in the system. This leads to longer waiting times and fees for transfers, especially cross-border payments and is made worse by the fact that there are often more than three intermediaries in a single transaction.
According to Visa, financial institutions have very few correspondent bank relationships. As a result, during transfers, the sending institution most likely will not have a correspondent relationship with the receiving institution. This is what complicates the entire transfer process especially when two or more financial institutions are involved in the transaction.
For example, a transfer from one country to another may involve domestic transfers within the sending country, an international transfer, and other transfers when the money arrives in the recipient country. At each of these points, the money will be subject to third party clearing as well as handling and may take days to reach the recipient finally.
Visa believes that a digital asset network like the one used by several cryptocurrencies can be a great solution to the problem. The company has shared its plans to launch another platform that will use blockchain technology to facilitate the transfer of digital assets from one client to another. This can be in the form of payments, transfer, and access to digital rights, personal credentials amongst other things. Network participants will be pre-screened legitimate organizations that will be expected to comply with the rules of the platform.
Visa B2B Connect Explained
Visa B2B Connect is a payment service that facilitates payment transactions between businesses. The company is currently testing its pilot technology to ensure that it works seamlessly before it is released to the public.
The B2B Connect platform will provide a way for clients and vendors to be paid without the hassle of third party involvement. The platform is rooted in blockchain technology and has already enrolled some financial institutions including the U.S Commerce Bank, Singapore’s United Overseas Bank, South Korea’s Shinhan Bank and the Union Bank of Philippines.
The platform will function by providing users with tools that they can easily use to make their payment processes easier. Through this platform, Visa hopes to completely change the way cross-border and cross-currency payments are done.
The platform is designed to be simple, fast and secure with an inbuilt permissionless private network. Scalability has also been considered in the creation of the platform due to the potential adoption rate of such a technology. Management of transactions on the network will be handled end-to-end by Visa according to its standard practices.
How Does Visa B2B Connect Work?
Just like Mastercard’s blockchain solution, the Visa B2B Connect consists of a group of APIs that allow participating financial institutions to automate all their B2B, cross-border payments.
According to the patent filed by Visa, the platform consists of a method and system which automate the transfer of digital assets in a digital asset network. Users on the network are enrolled and screened for eligibility and compliance before they can fully use the services on the platform.
The entire process of using the Connect platform is transparent and consists of standardized transfer processes and unique identifiers. Digital signatures can also be stored along with digital assets to ascertain a value for those assets.
Customers on the network, most likely banks, can integrate their normal operations with the Visa B2B Connect APIs to develop end-to-end B2B payments solutions. This way, it’s easier for such institutions to onboard their customers, set up their suppliers and manage foreign exchange rates as well as payment submissions. They can also use the the APIs to solve more specific problems like checking the status of payments initiated on the bank-specific Visa B2B Connect site. The platform provides the following APIs:
Bank API
Visa’s bank API gives banks the opportunity to manage their settings and profile information as well as view current and past net settlement positions of transactions processed on Visa B2B Connect. It also allows banks to search for companies that they previously enrolled on their Visa B2B Connect service.
Company API
This is the API that allows participating banks to register new companies on their Visa B2B Connect platform as well as manage their previous and current enrollments. It also helps the bank to determine whether a registered company’s supplier is also registered on the service and is eligible for payment.
Payments API
So-called, the payment API will allow banks and other financial institutions to initiate a payment on behalf of its registered customer to one of that customer’s enrolled suppliers. It also allows the bank to search for any Visa B2B Connect payments made or received by its registered companies and view the present or past foreign exchange rate for a given currency pair. This way, companies can be shown the foreign exchange rate before they make cross-currency payments.
Usually, the foreign exchange rate calculator requires the bank to enter the source and target currency ISO codes. Upon provision of a specific date, the foreign exchange response will contain the Visa B2B Connect foreign exchange rate for the requested day.
Reference Data API
The Reference Data API shows participating banks a list of countries that not eligible to join the Visa B2B Connect service. They can also view the system level limits for Visa B2B Connect Transactions, the different types of transactions and currencies supported by Visa B2B Connect, available bank payment notification options, and industry classification codes.
During the onboarding process, these codes help the bank to identify the industry a company falls under. The reference data API also contains an API explorer which can be used to understand the uses of each API on the platform better.
Why Use the Visa B2B Connect Platform?
Visa has shown through previous achievements that it can create technological solutions that are beneficial to users in so many ways. The B2B Connect platform is no different, and users can expect the following benefits from it:
- Transparency: The platform is transparent and predictable, both qualities that are valuable and highly necessary in the financial industry. Participating institutions along with their clients receive notifications of transactions in real-time.
- Security: All transactions on the network are signed and linked cryptographically o ensure immutability of records in the system.
- Trust: Every participant in the network is known and can be identified by Visa.
Mastercard Blockchain vs. Visa Blockchain
While both corporations have decided to adopt and apply blockchain technology, there is a significant difference between the problems that each one is trying to solve.
Mastercard has focused on the issue of credit card skimming by creating a private network solution for the transfer, encryption, and verification of a user’s credentials to avoid theft. This approach makes transactions between vendors and clients safer, thereby focusing mainly on security.
Visa, on the other hand, aims to tackle the friction between third parties when a cross-border transfer is initiated. Although individuals have gotten used to the wait time experienced during wire transfers, Visa finds it unnatural. These long wait times slow business down and waste valuable time.
For example, if a businessperson has to wait five days for a wire transfer before shipping goods, it translates to a waste of time compared to a scenario in which wait time is only a few minutes. Through its B2B Connect platform, Visa hopes to solve this problem by providing access to its APIs for businesses to transfer money on its network without the need for clashing intermediaries.
Both companies have managed to implement blockchain technology without necessarily being in direct competition with each other. However, Mastercard has significantly higher stakes in the use of the technology. Apart from securing almost 30 patents, its collaborations with other companies as well as significant partnerships towards blockchain adoption prove this.

Final Thoughts
Mastercard and Visa have made significant strides in the blockchain industry and the financial sector as a whole. However, competitors like American Express are fast on their heels with numerous patents in blockchain related inventions.
Mastercard continues to lead by a long shot, despite Visa’s patented “digital asset network.” The details of several Mastercard blockchain patents are still unclear, but there is a lot of anticipation in the ecosystem about what the company will dish out in the future.
Although these financial industry giants have adopted blockchain, expecting others in the industry to follow suit is a stretch. The industry is founded on the principles of central authorities and directly contrasts the decentralized concepts of cryptocurrency as a whole.
However, the moves by these financial solutions providers, show that the future of money may indeed resemble Bitcoin. If this happens, paper money may be completely eradicated, and transactions will be carried out on peer consensus-driven networks. It may take a while for traditional institutions to come around, but there is still hope as the cryptocurrency industry continues to develop.
It is expected that Mastercard, Visa, and other large corporations will continue to file blockchain patents as research progresses. In general, innovation within the industry is happening at a fast pace seeing as banks like J.P.Morgan are already venturing into it. Huge venture capitalists like the Rockefellers have also announced their foray into the industry.
Even in these early days, it is clear that blockchain is here to stay. In the future, the technology will be ingrained into everything humans do, from payments to communication to commerce. For now, Mastercard is ahead of other financial corporations concerning blockchain innovation. Hopefully, Visa will recognize the competition and catch up. Either way, innovation from all angles is great for the consumers.
Originally posted on MintDice.com